How do I choose a coil tubing size?
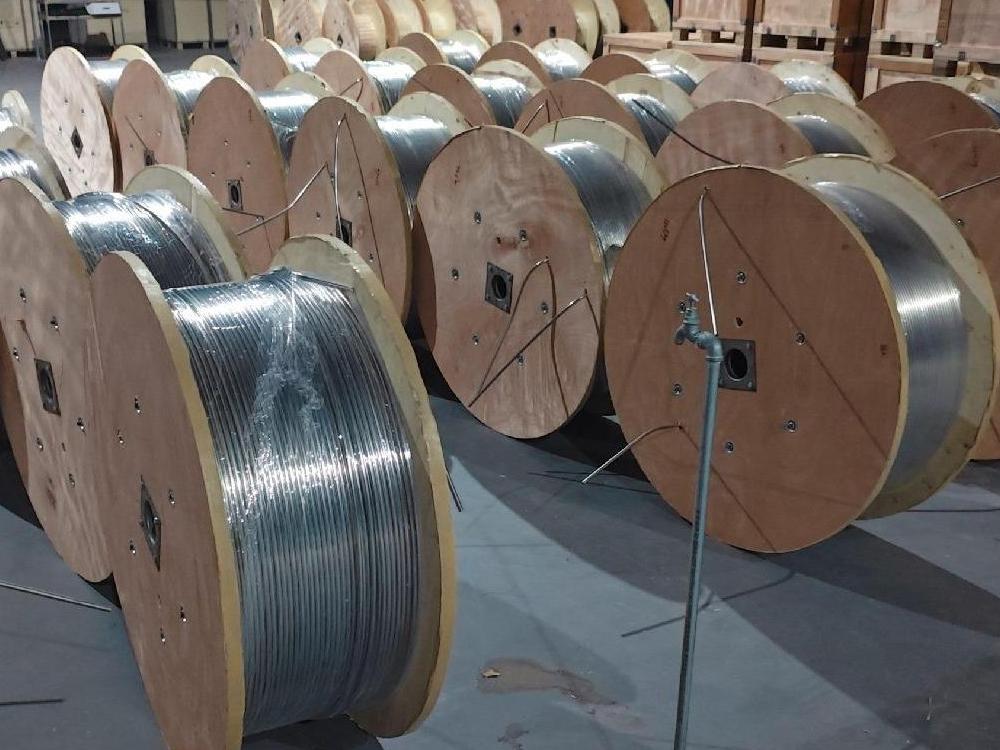

—Key Factors in Selecting the Right Diameter, Wall Thickness, and Material for Your Application
How to correctly select the coil size is the key to ensure the efficient and safe operation of the industrial fluid transmission system. This article introduces the key factors for selecting coil size, including inner diameter, wall thickness, length, use environment, etc.
Coiled tubing (CT) is a new type of oil pipe material with a single length of several kilometers and can be bent repeatedly and achieve multiple plastic deformations. Due to the diversity, speed and reliability of coiled tubing operations, coiled tubing and its operating equipment are called "universal operating machines". So how to choose coiled tubing is an important issue. Here are some suggestions:
1. Inside diameter (ID)
The inside diameter directly affects flow rate and pressure drop. Larger inside diameters are required for high-flow operations (such as hydraulic fracturing) to reduce friction losses and maintain system stability; smaller inside diameters are suitable for low-flow operations (such as nitrogen injection) or space-constrained scenarios. It is necessary to ensure that the tubing is compatible with the downhole tools and wellbore dimensions.
2. Wall thickness
The wall thickness is determined by the operating pressure and safety margin. High-pressure operations (such as deep well intervention) require increased wall thickness to prevent collapse or bursting. Calculate the minimum wall thickness according to API/ASME standards and add a safety factor (usually 1.2–1.5). Note: Increased wall thickness reduces flexibility and may limit passability in inclined or horizontal wells.
3. Length
Longer tubing can reduce the number of connection points and reduce the risk of leakage. However, extra-long pipe sections (such as more than 30 meters) will increase the difficulty of transportation and installation. It is recommended to use a modular design with standardized lengths and quick connectors to balance reliability and operability.
4. Material and environmental adaptability
Choose materials according to the environment.
Corrosive fluids: Use corrosion-resistant materials or coatings such as stainless steel and nickel-based alloys.
High temperature environment: Ensure that the material maintains strength at the operating temperature (e.g., use quenched and tempered steel above 150°C).
High pressure environment: Increase wall thickness or use composite reinforced pipes.
5. Bending radius
The minimum bending radius must match the tubing diameter and material properties. If the bending radius is less than 5 times the pipe diameter, permanent deformation or fatigue cracks may occur. In complex wellbore trajectories, it is recommended to simulate the pipe stress through finite element analysis (FEA).
As a coiled tubing product expert, MTSCO is committed to providing you with reliable quality and reasonably priced products and services. Our product range covers welded coiled tubing and control lines. If you have any questions or needs, please feel free to contact us. We are happy to provide you with comprehensive support.
Related Products
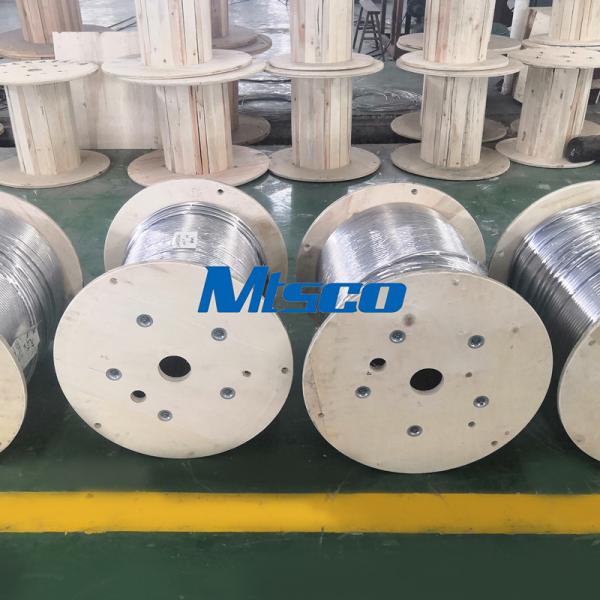

Bright Annealed Stainless Steel Coiled Tubing Seamless Tube For Industry
stainless steel coiled tubing is a kind of pipe that can be widely used in petrochemical, electric power, nuclear industry, medicine, food, and other industries....
Downhole Tools TP316/TP316L Seamless Stainless Steel Coiled Tubing
Maybe someone also calls it control line, capillary tubing, downhole tubing, chemical injection tubing, etc. Because the welded coiled tubing can be used in a variety of applications.Such as Marine, oil and gas, downhole, heat exchanger......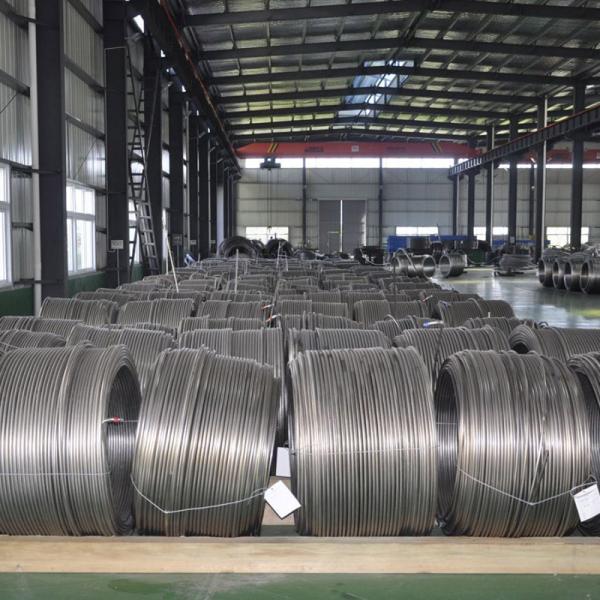

 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
